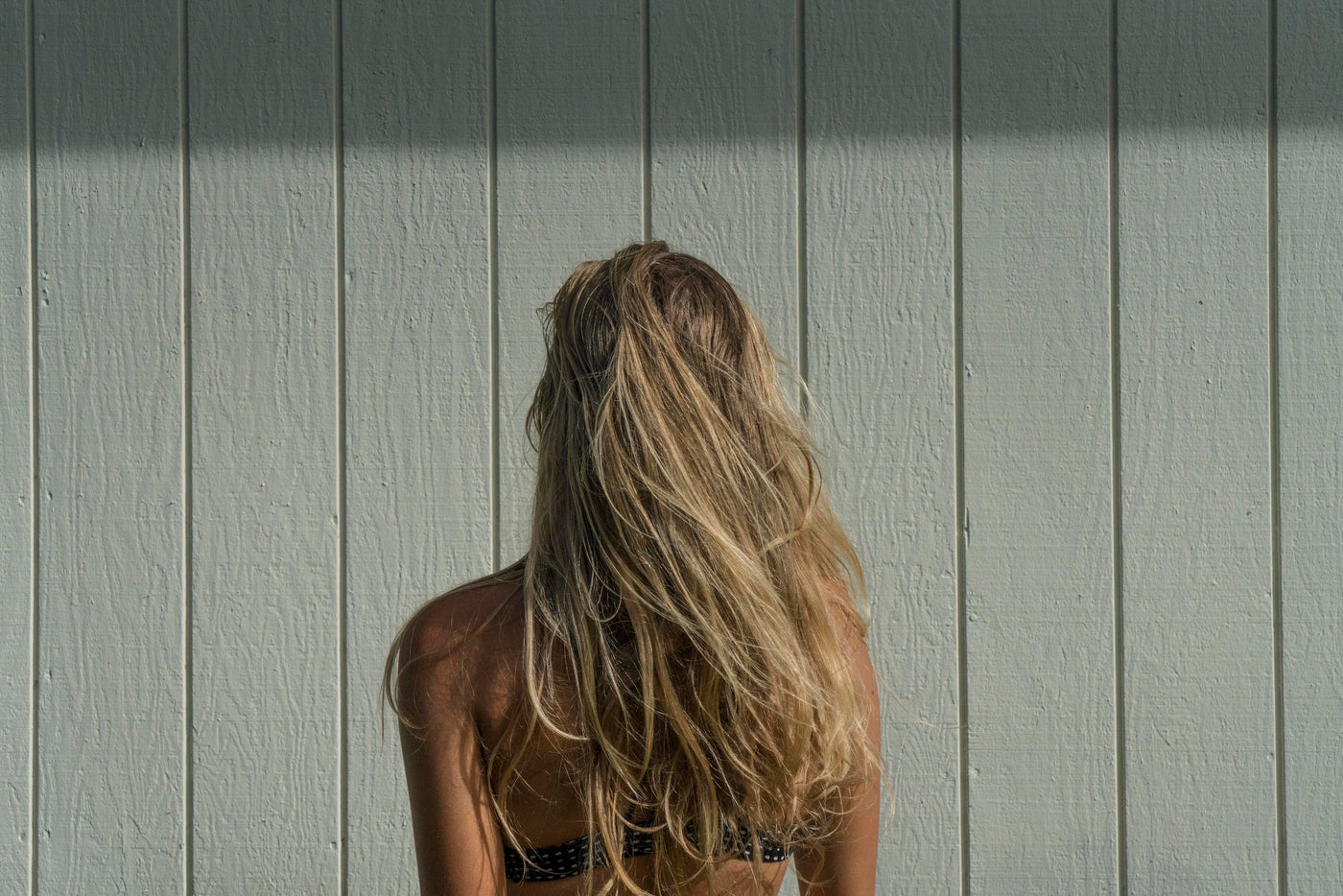
Hair loss is a common problem
There are dozens of different reasons for premature hair loss and weakened hair growth. They can be genetic, hormonal, or due to stress, menopause, and diseases. About 85% of men and 60% of women suffer from premature hair loss. With the right treatments, hair loss can be stopped and growth reactivated.
Skin Clinic Kuulas offers you solutions to overcome hair problems. The unique products of Mark Birch combined with scalp needling using the next-generation Dermapen 4 device are the core of our service.
Here's how to proceed:
1. Contact us through the chat in the lower right corner or you can also reach us through the new unique Iholinja video consultation.
2. Choose the right Mark Birch products for you to start home care
3. Book an appointment for scalp needling, during which we will assess your situation and future plan to achieve the best possible results
4. Monitor the results and update the plan as needed.
INFORMATION ABOUT HAIR LOSS
Hair loss can be stopped and growth reactivated by first identifying the causes
- Hormonal / Metabolic
- Chemical
- Physical
Heredity (Hormonal / Metabolic)
Male and female pattern hair loss are hereditary forms of hair loss caused by male hormones, affecting up to 50% of men and 30% of women. About 20% of men start the process at the age of 20 or even earlier. Among 30-year-old men, 30% already suffer from the condition, and so on. For women, the process often begins around the age of 30. The rate of progression of baldness and hair loss varies from person to person. Often, the process lasts for years or even decades. The younger the hair loss begins, the faster it usually is. The majority of Finns aged 40-65 suffer from hair loss to some extent.
The cause of hereditary hair loss is the male hormone DHT or dihydrotestosterone (5-alpha-dihydrotestosterone). It is produced from testosterone and the 5-alpha reductase enzyme in the testes and prostate, as well as in the hair follicle. Both men and women can lose hair due to changes caused by this hormone in the body. DHT shrinks hair follicles, weakens hair, and shortens the hair growth cycle. If the DHT level is high during the hair's resting phase, it may completely prevent the formation of new hair.
Aging (Hormonal / Metabolic)
With age, the amount of hair decreases steadily as the hair growth phase shortens and the resting phase lengthens. Hair thins and becomes finer, and they no longer grow as long as they did when young. Especially for women, hair thinning may affect volume even more than the reduction in their number.
Aging also affects hair color, texture, growth, and density. An aging hair follicle produces less melanin, resulting in hair graying. Graying can sometimes start before the age of thirty, usually from the temples and the top of the head. The speed of graying partly depends on genetic factors. By the age of 40, 40% of people have some gray hair. People of European descent gray earlier than Asians. Hair also thins as a person ages, partly due to the reduction in the pigment melanin.
Menopause and hormones (Hormonal / Metabolic)
With menopause, a woman's body's production of estrogen decreases and eventually stops completely. The amount of estrogen has a clear connection to the good condition of the hair and scalp, as well as the rest of the skin. As the amount of estrogen, which maintains the good condition of the skin and hair, decreases, the relative proportion of male hormones that promote hair loss increases and may accelerate hair loss in its own right. Due to menopause, the skin and scalp dry out and thin and lose their elasticity. With the changes occurring in the skin, the hair follicle becomes lazy, and the blood circulation in the scalp slows down.
Pregnancy and breastfeeding (Hormonal / Metabolic, Physical)
During pregnancy, the blood estrogen level is very high. As a result, many expectant mothers' hair is in good condition and grows more vigorously than usual. 1–3 months after childbirth, estrogen levels decrease to almost menopause levels, and more hair starts to fall out than usual. Changes in hair condition after childbirth are therefore very common. The length of breastfeeding, the diversity of nutrition, and individual factors that strain the body affect when the estrogen level returns to normal. After childbirth, the hormonal balance returns to normal.
A healthy and varied diet and supplements help the body recover from the changes brought by pregnancy and breastfeeding and also promote hair growth. Hair growth can also be enhanced with products that extend their growth phase.
Stress, hurry, and insomnia
(Hormonal / Metabolic, Physical)
Stress and lack of sleep strain the body, increase stress hormone levels, and weaken blood circulation in the scalp. This results in poor oxygen and nutrient supply to the hair follicles and roots, preventing hair from getting the building blocks needed for development.
Dieting, unbalanced diet, and nutrient absorption disorders(Chemical)
For the hair follicle to function actively, it must receive enough amino acids, vitamins, iron, and minerals and trace elements daily. Dieting, an unbalanced diet, absorption disorders, and soil depletion can affect the availability of nutrients and protective nutrients in the scalp. Hair is about 80% protein, emphasizing the importance of protein in the diet. If necessary, the diet should be supported with supplements and vitamin preparations.
Diseases and treatments, surgeries, and traumas
Severe general diseases, autoimmune diseases, infections, high fever, as well as traumas and surgeries can trigger hair loss, as can scalp skin diseases like psoriasis, atopy, fungal dandruff, and fungal infections. Strong treatments like chemotherapy and radiation therapy, as well as X-ray examinations, also affect hair loss.
Often, hair grows back once the disease is treated, but it may be thinner and lighter in color.
Medications(Chemical)
Some medications can cause hair loss as a side effect. Chemotherapy drugs used in cancer treatment, antidepressants, painkillers, birth control pills, blood thinners, and blood pressure medications may cause hair loss and thinning. Certain medications, such as cortisone, have a drying and thinning effect on the scalp, indirectly weakening scalp health and hair growth.
Environmental factors, smoking, and alcohol(Chemical)
Air pollution, active and passive smoking, excessive alcohol consumption, and processed food containing additives weaken the nutrition supply to hair and may promote hair loss.
The load of styling products on the scalp and repeated strong hair treatments(Chemical)
Residues from styling products, impurities, sweat, sebum, and dead skin cells are a greater burden on hair and scalp than washing, as they can interfere with hair growth. Disruptive factors are removed with careful and gentle daily washing. If the scalp is dry, sensitive, itchy, or burning, special attention should be paid to its care and product selection.
Hair treatments like coloring strain the hair and scalp. Therefore, treatment intervals should be extended to 6-8 weeks and always done by a hairdresser. At home, hair should be washed gently daily, brushed gently with a brush with rounded bristles, and allowed to dry naturally or dried and styled gently at low temperatures.
MOST COMMON SCALP DISEASES AND IMBALANCES
Only healthy and nourished scalp grows healthy hair, so scalp diseases and imbalances weaken active hair growth. Additionally, scratching an itchy scalp may damage hair roots and increase hair loss. Healing an irritated scalp and achieving balance is of utmost importance.
Dandruff
Dandruff is one of the most common scalp problems, with up to 65 percent of people suffering from it at some point in their lives. For most, the problem is recurring. The cause of dandruff is usually an overgrowth of the yeast fungus malassezia on the scalp, which irritates the skin so that the irritated skin begins to produce new skin cells too quickly. There can be many reasons behind dandruff, but common to all types of dandruff is the disturbing, flaky dandruff falling from the scalp and itching. When the symptoms of dandruff include light and visible flakes, dry scalp, and possible itching, it is dry dandruff. If the flaky scalp becomes oily easily and the dandruff flakes accumulate into yellowish clusters, it is oily dandruff.
Sensitivity, itching, and dryness
Scalp itching, tingling, tightness, warmth, and tenderness are common problems. According to a French study, 41 percent of men and 47 percent of women feel they have a sensitive scalp. Sensitization can be triggered by many factors, such as scented and colored hair care products and the chemicals they contain: such as silicones and pearls. Also, too infrequent washing intervals, insufficient rinsing after washing, weather changes, dry indoor air, stress, and chemical treatments may cause irritation.
Oily scalp
An oily scalp is a common ailment. About one-third of Finns have excessive sebum secretion. Bacteria and yeasts transform the sebum into a more liquid form, and the hair becomes greasy quickly. The oiliness makes the hair look sticky and flat. Despite regular washing, the hair also starts to smell. An oily scalp requires more frequent hair washing and a shampoo that effectively removes sebum. In this case, too, a common mistake is to stretch the washing intervals. Contrary to belief, more frequent washing does not increase oiliness, but with the right shampoo, sebum secretion can be reduced.
Psoriasis
Psoriasis causes intense flaking and crusting on the scalp. The skin flakes, and under the dandruff, there are red patches. Usually, the skin shows symptoms elsewhere than just the scalp. Psoriasis is a common problem, estimated to affect about 3% of the population. Scalp psoriasis can appear in mild form as small patches, but it may also manifest as large, red, and flaky areas, which may also experience hair loss. The cause of psoriasis is not known for certain. It is suspected to be an autoimmune reaction.
Atopic dermatitis or eczema
Eczema is an inflammatory skin disease that usually appears in infancy, calms down during childhood, but can worsen again in adulthood. In adolescents and adults, it most often manifests in the head area and upper body. Most skin changes are thickening of the skin's surface layer caused by scratching, crusts, and small wounds. Often there is also a chronic infection caused by staphylococci and other pus bacteria.
Seborrheic Dermatitis
Seborrheic dermatitis, also known as seborrheic eczema, is a common problem affecting 15-20% of the population. One in three Finns has oily skin, more often in men than in women. Certain bacteria and yeast fungi that are part of the skin's normal flora break down sebum. The sebum becomes rancid, and rancid sebum irritates the skin. The irritation feels like itching and burning, the skin begins to redden and flake. Those suffering from seborrheic dermatitis The skin can be both oily and dry at the same time.
Treatment of scalp problems
A common mistake is to reduce the frequency of hair washing when scalp problems occur. The scalp is a large skin area and secretes about a teaspoon of oil and sweat in a day. Therefore, unwashed scalp quickly accumulates toxins, oils, dead skin cells, and dirt as well as residues of styling products.
When there are problems, imbalances, or diseases in the scalp, the treatment always starts by increasing the frequency of washing. The scalp should preferably be washed daily as long as the shampoo is appropriate.
For severe scalp problems, Triple Action Scalp Therapy Shampoo is used. Thanks to its active ingredients, the shampoo alleviates skin irritations, soothes a flaky scalp, and helps reduce the formation of dandruff. It also deep cleanses and opens hair roots. It is particularly suitable for those suffering from hair loss.
For milder scalp problems (dandruff, itching, irritation, dryness, sensitivity), R&B Antioxidant Shampoo is used. It also soothes and prevents itching and irritation.